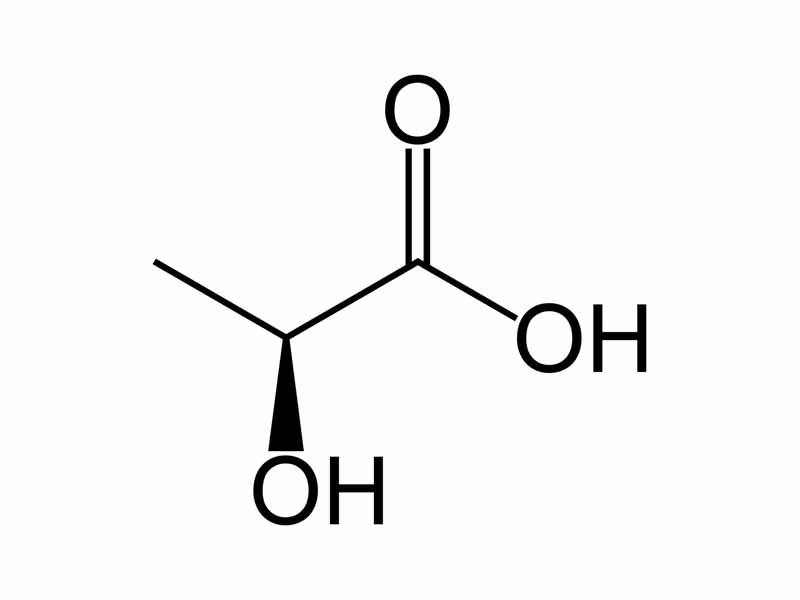
Interdisciplinary Note (3 of 5)
Lactate is produced in skeletal muscle by reduction of pyruvate by NADH. The purpose is to recycle NAD+ in order to carry on the oxidation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate in glycolysis. Anaerobic metabolism nets the skeletal muscle cell two ATP per glucose. The lactate then serves as a precursor for glucose in the liver in gluconeogenesis, which costs six ATP per glucose. Lactic acid fermentation shifts the metabolic burden from the muscle to the liver.