Sleep Disorders
- Dyssomnias are a broad classification of sleeping disorders that make it difficult to get to sleep, or to remain sleeping.
- Parasomnias are a category of sleep disorders that involve abnormal movements, behaviors, emotions, perceptions, and dreams that occur while falling asleep, sleeping, between sleep stages, or during arousal from sleep.
- Insomnia, also known as trouble sleeping, is a sleep disorder in which there is an inability to fall asleep or to stay asleep as long as desired.
- Rebound insomnia is the emergence or re-emergence of insomnia symptoms that were either absent or controlled while taking a medication, but appear when that same medication is discontinued, or reduced in dosage (at often a worse level of severity than pretreatment levels).
- Restless legs syndrome is a neurological disorder characterized by an irresistible urge to move one's body to stop uncomfortable or odd sensations.
- Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder involving the loss of the brain's ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles normally. People with this condition experience frequent excessive daytime sleepiness.
- Cataplexy is a sudden and transient episode of muscle weakness accompanied by full conscious awareness, typically triggered by emotions such as laughing, crying, terror, etc. It is the cardinal symptom of narcolepsy.
- Orexin, also called hypocretin, is a neuropeptide that regulates arousal, wakefulness, and appetite. The most common form of narcolepsy is caused by a lack of this substance in the brain due to destruction of the cells that produce it.
- Sleep paralysis is a phenomenon in which a person either during falling asleep or awakening, temporarily experiences an inability to move, speak, or react. One hypothesis is that it results from disrupted REM sleep, which normally induces complete muscle atonia.
- Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or instances of shallow or infrequent breathing during sleep.
- A night terror is a sleep disorder, causing feelings of terror or dread, and typically occurs during the first hours of stage 3 non-REM sleep. They tend to happen during periods of arousal from delta sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep.
- Somnambulism is a sleep disorder belonging to the parasomnia family. Sufferers arise from the slow wave sleep stage in a state of low consciousness and perform activities that are usually performed during a state of full consciousness.
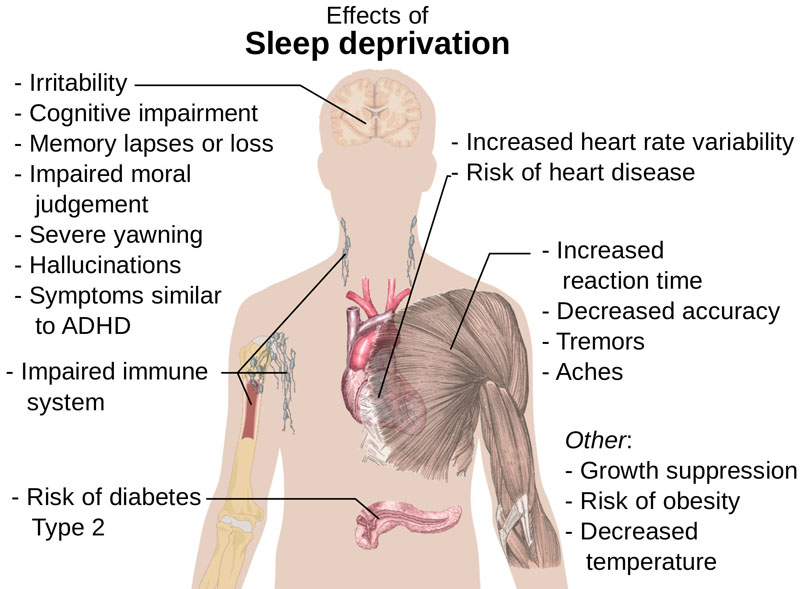
- Sleep deprivation is the condition of not having enough sleep; it can be either chronic or acute.
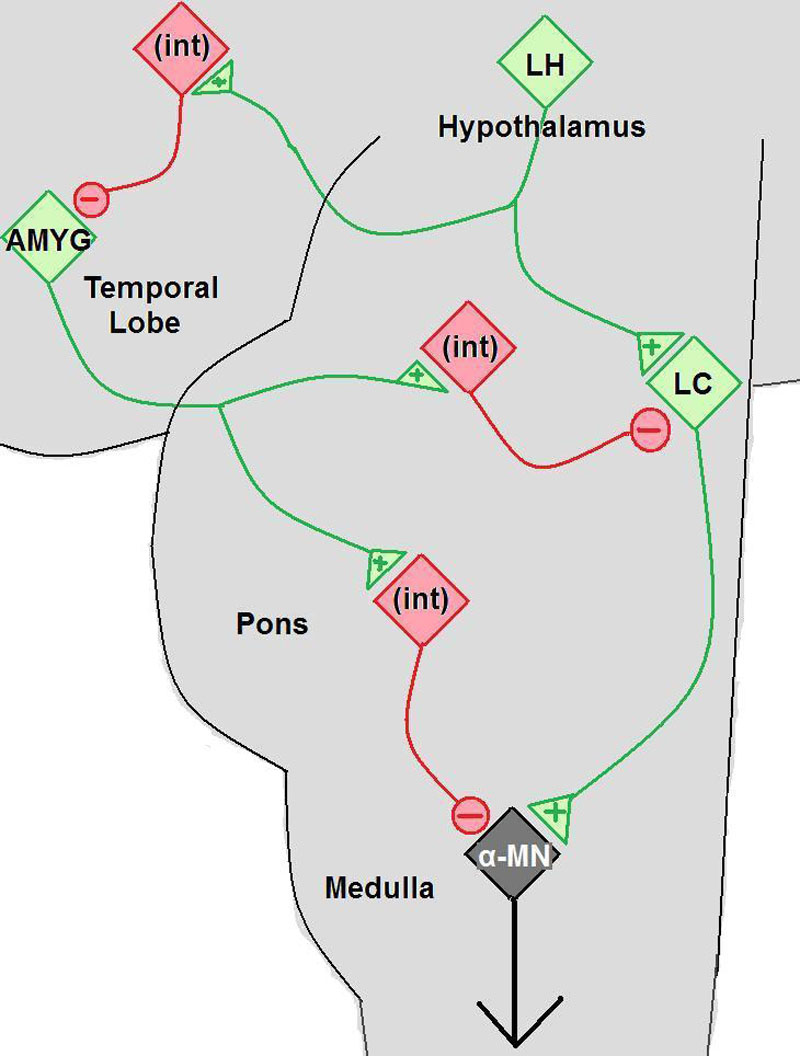
In this simplified brain circuit, damage to orexin-secreting neurons in the hypothalamus can lead to inhibition of motor neurons, thus lowering muscle tone.