Depressant Drugs: Alcohol and Sedative-Hypnotics
- A sedative or tranquilizer is a substance that induces a state of calm or sleep by reducing irritability or excitement.
- A hypnotic is a type of psychoactive drugs whose primary function is to induce sleep. They are used in the treatment of insomnia (sleeplessness) or surgical anesthesia.
- A GABA receptor agonist is a drug that binds one or more of the GABA receptors, producing typically sedative effects.
- A GABA receptor positive allosteric modulators is a type of drug that affects a subtype of GABA receptor by binding at a different site than the active site. Examples include ethanol, benzodiazepines, and the barbiturate drugs.
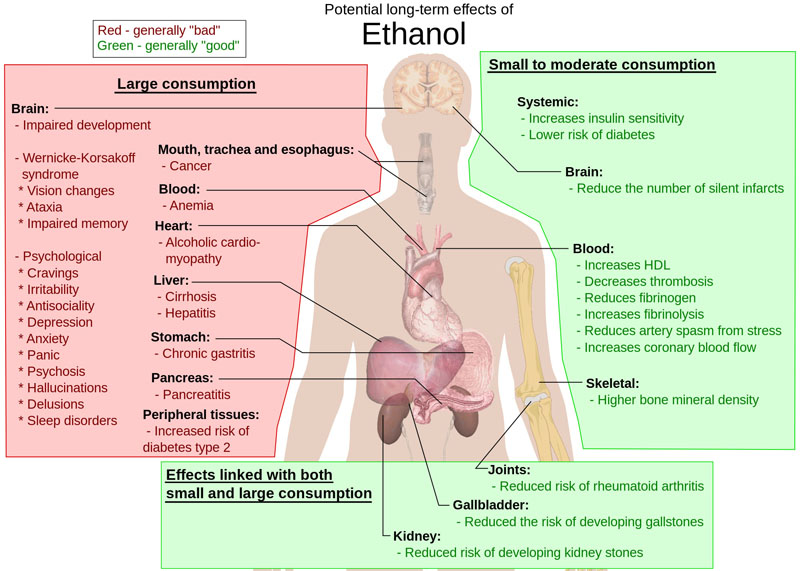
- An alcoholic beverage is a drink which contains a substantial amount of the psychoactive drug ethanol.
- Alcoholism, also known as alcohol use disorder and alcohol dependence syndrome, is a broad term for any drinking of alcohol that results in problems.
- Alcohol myopia is a cognitive-physiological theory on alcohol abuse in which many of alcohol's social and stress-reducing effects are explained as a consequence of alcohol's narrowing of perceptual and cognitive functioning.
- Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome is a manifestation (separate or concurrent) of thiamine deficiency, encephalopathy, and psychosis. Usually secondary to alcohol abuse, it mainly causes vision changes, ataxia and impaired memory.
- Delirium tremens is a state of confusion of rapid onset usually caused by withdrawal from alcohol. Physical effects may include shakings, shivering, an irregular heart rate, and sweating. Occasionally a very high body temperature or seizures may result in death.
- Alcoholic hallucinosis (or alcohol-related psychosis or alcohol-induced psychotic disorder) is a complication of alcohol withdrawal in alcoholics.
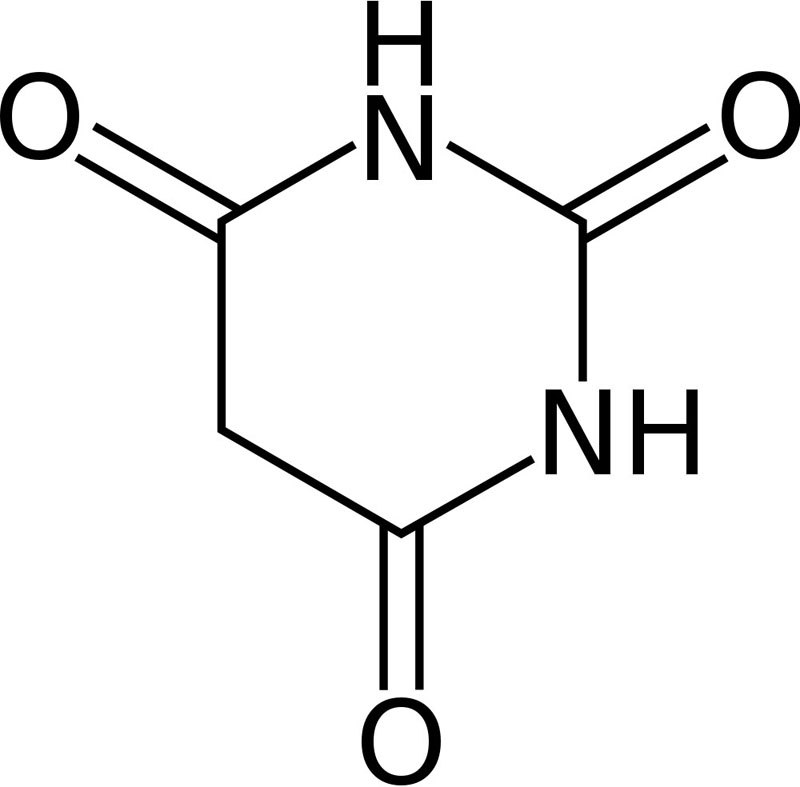
- Derivatives of barbituric acid, barbiturates are drugs that act as central nervous system depressants, and can therefore produce a wide spectrum of effects, from mild sedation to total anesthesia.
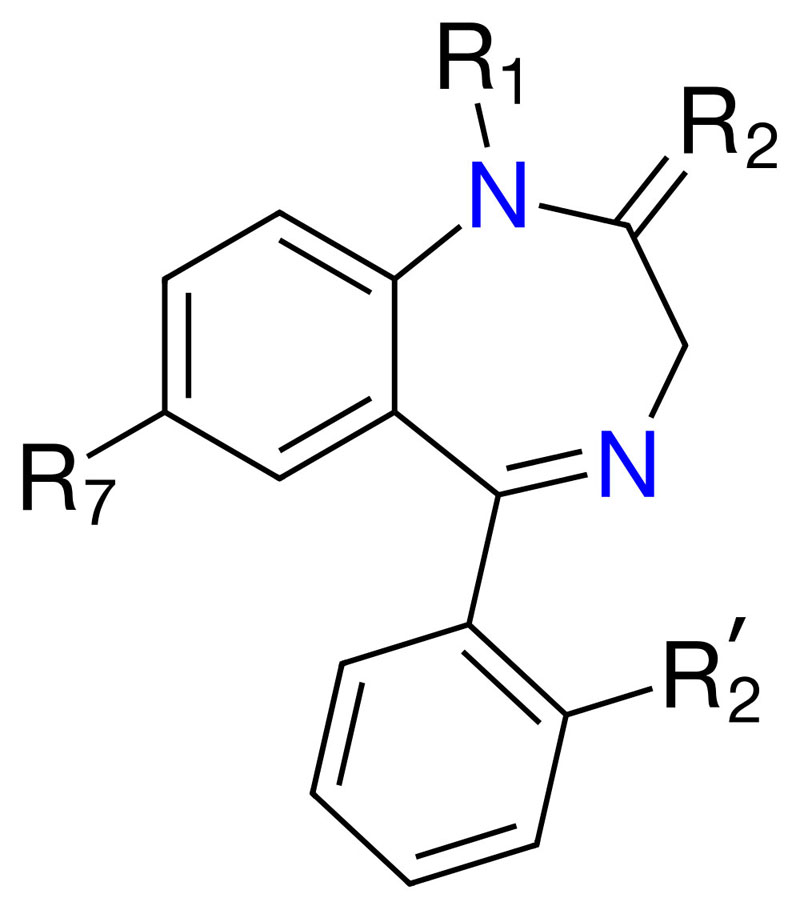
- Benzodiazepines are the class of drugs that include valium and clonazepam, which enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), resulting in sedative, hypnotic, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant effects.
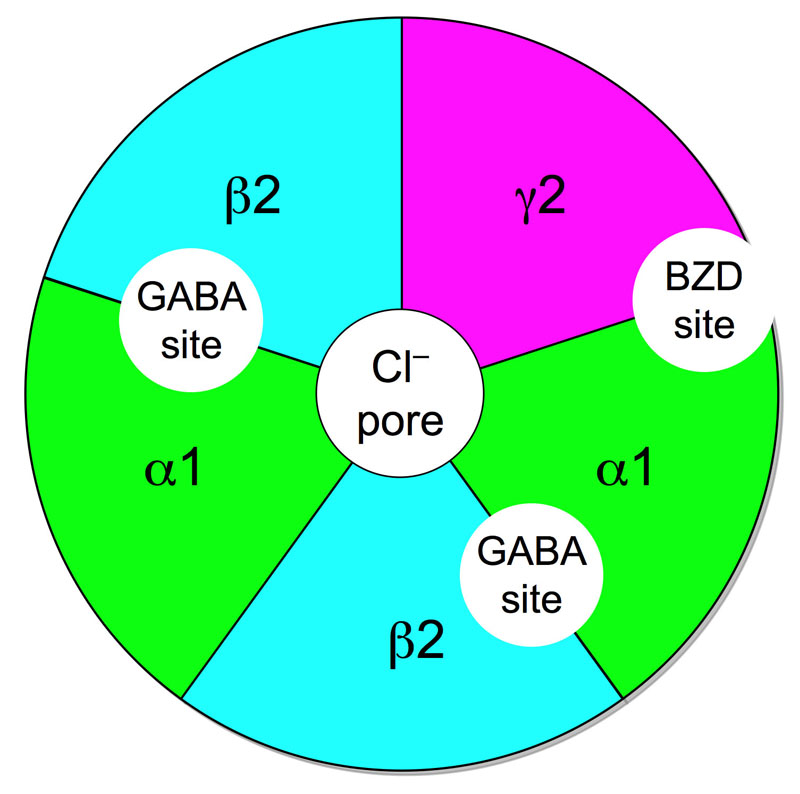
Schematic diagram of a GABAA receptor protein ((α1)2(β2)2(γ2)) which illustrates the five combined subunits that form the protein, the chloride (Cl–) ion channel pore, the two GABA active binding sites at the α1 and β2 interfaces, and the benzodiazepine (BZD) allosteric binding site at the α1 and γ2 interface.