Interdisciplinary Note (3 of 29)
The reactions of aldehydes and ketones are among the most important both for the organic chemistry course and for the MCAT. To keep the reactions of aldehydes and ketones straight, keep in mind that most reactions of aldehydes and ketones belong to one of two classes, those involving nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon and those involving electrophilic attack on the α carbon.
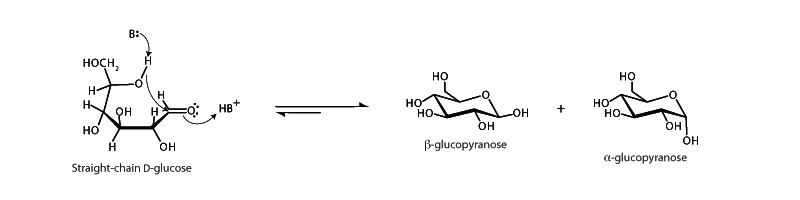
Aldehydes and ketones are subject to nucleophilic attack at the carbonyl carbon because the carbonyl group of an aldehyde or ketone is polar. Resonance also contributes to the reactivity of the group. The electronegativity of oxygen is 3.5 while carbon is 2.5, so bonded to oxygen, the carbonyl carbon obtains a partial positive charge. Additionally, resonance also leads to delocalization of the π bonding electrons onto the oxygen, endowing oxygen in this resonance form with a -1 formal charge and carbon a +1 charge, which contributes to the polarity of the bond.
In addition to nucleophilic attack of the carbonyl carbon, aldehydes and ketones may also undergo reactions of a second major type, which depend on the interconversion of aldehydes and ketones with their enolate isomers. This interconversion leads to the susceptibility toward attack by electrophiles at the α carbon. An aldehyde or ketone must possess at least one α hydrogen to undergo reactions of this second type.