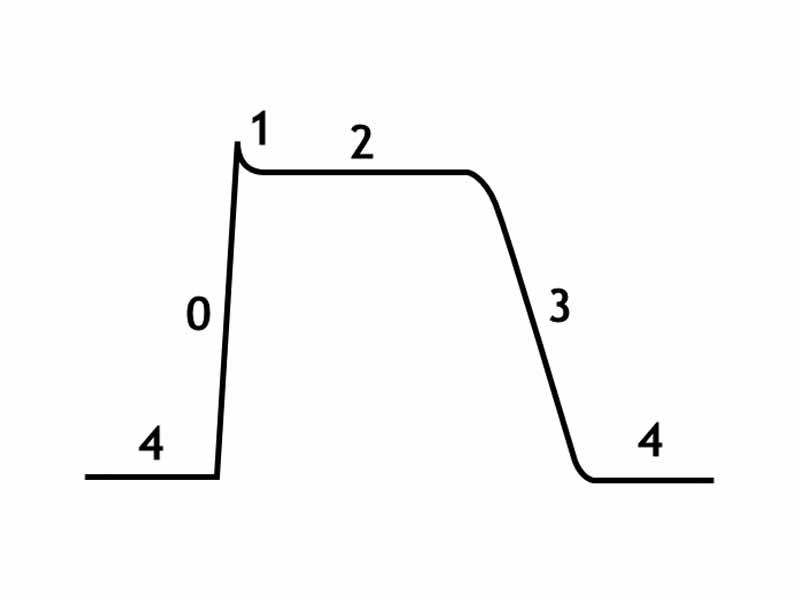
The cardiac action potential has five phases. Phase 4 is the resting membrane potential. Phase 0 is the rapid depolarization phase. Phase 1 of the action potential occurs with the inactivation of the fast Na+ channels. Phase 2: This plateau phase of the cardiac action potential is sustained by a balance between inward movement of Ca2+ (ICa) through L-type calcium channels and outward movement of K+ through the slow delayed rectifier potassium channels, IKs. During phase 3 of the action potential, the L-type Ca2+ channels close, while the slow delayed rectifier (IKs) K+ channels are still open.
Click this LINK to visit the original image and attribution information. Right click on the image to save the 800px teaching JPEG.