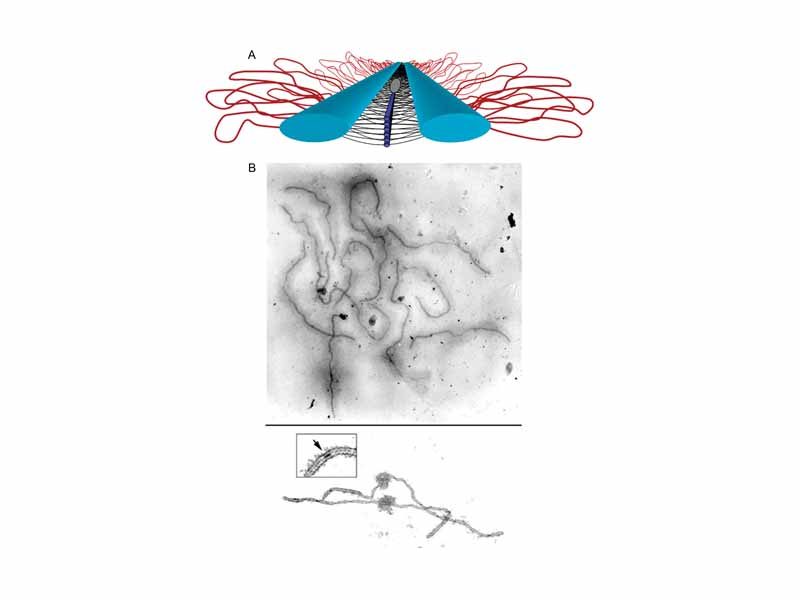
The Synaptonemal Complex. (A) Model of the SC. Lateral elements (light blue rods) of homologous chromosomes align and synapse together via a meshwork of transverse filaments (black lines) and longitudinal filaments (dark blue rods). The longitudinal filaments are collectively referred to as the central element of the SC. Ellipsoidal structures called recombination nodules (gray ellipsoid) are constructed on the central region of the SC. As their name implies, recombination nodules are believed to be involved in facilitating meiotic recombination (crossing over). The chromatin (red loops) of each homologue is attached to its corresponding lateral element. Because there are two sister chromatids in each homologue, two loops are shown extending laterally from each point along a lateral element. (B) Top: Set of tomato SCs. Chromatin sheaths are visible around each SC. Bottom: Two tomato SCs. The chromatin has been stripped from the SCs, allowing the details of the SC to be observed. Each SC has a kinetochore (ball-like structure) at its centromere. Recombination nodules, ellipsoidal structures found on the central regions of SCs, mark the sites of crossover events (see inset).
Click this LINK to visit the original image and attribution information. Right click on the image to save the 800px teaching JPEG.